Websites and web applications Published on by Chloé Chassany
WordPress user roles, their permissions, and how to manage them

If you have already worked with WordPress, you probably know that each user is assigned a specific role. User roles are essential for all types of WordPress sites, including blogs, showcase sites, and online shops.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, this article will help you better understand user roles in WordPress.
What is a WordPress user role?
To get off to a good start, here is the definition found in the WordPress documentation:
A role defines a set of tasks that a person assigned to that role is authorised to perform.
This person therefore has specific authorisations according to the role assigned to them.

What are the different user roles on WordPress?
Depending on the project (standard website, e-commerce website with WooCommerce, or multisite), there may be more or fewer user roles:
- For a standard site, there are five default user roles: Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor, and Subscriber.
- On a site where WooCommerce is installed, two user roles are added: Shop Manager and Customer.
- In the case of a multisite, all of the above roles may be present. An additional role is added: the Super Admin.
Take a look at the table below to see all the roles and permissions granted at a glance.
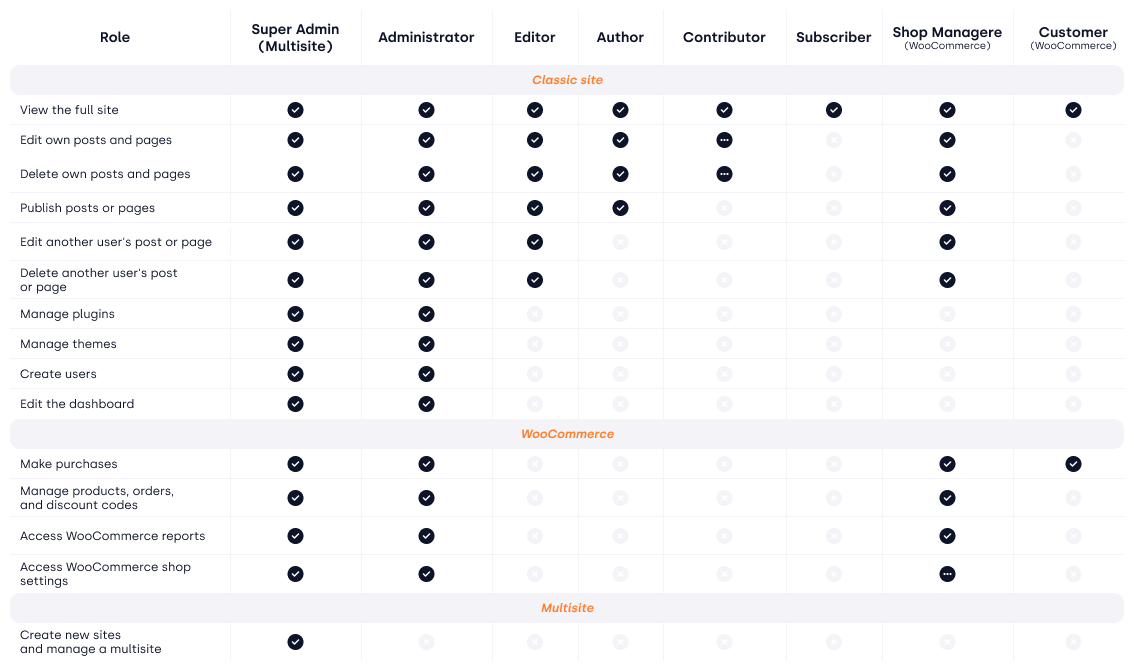
We will review them one by one and discuss the differences:
The Super Admin: the person who controls the entire network
Available only in a multisite network, the Super Admin has rights similar to those of the administrator, with one difference: they can manage multiple sites from a single location. This means they can add, modify or delete sites, themes, plugins, etc. on the network.
The Administrator, the one who controls the entire site
The administrator can do absolutely everything on a website, from management to publication.
They can modify the theme and plugins in place, manage users, modify menus, widgets, etc. In short, they can do everything and have access to the entire site. This is also the role assigned by default during installation.
The Editor, the editor-in-chief of your website
Located just below the administrator, this person is responsible for everything related to the content on the site: they can publish, edit, and delete articles, pages, or any other type of content as they see fit.
They will also be able to manage how items are organised into categories and tags using the same actions: customisation, modification, deletion. They can also manage comments in their entirety by approving, modifying or deleting them.
The Author, the creator of this whole affair
Authors can publish and manage articles without restrictions (we will look at contributors shortly).
They can write and publish articles, but unlike an editor, they cannot edit articles published by other people. However, they do not need any approval to publish.
They also have the option to manage comments posted on their articles.
The Contributor, the editorial intern
Consider contributors as interns: they can contribute to a site, but will need approval from an editor to have their articles published. They will not be able to edit or delete articles after publication.
One small issue with their involvement is that they cannot add images because they do not have access to the media library, but do not worry, there are solutions!
The Subscriber, relegated to the role of mere spectator
The subscriber is the role with the fewest permissions possible (apart from unregistered visitors).
Unlike other WordPress user roles, a subscriber cannot add any content. They can only edit their profile. This role can still be useful for sites with members (forums, clubs, etc.).
The Shop Manager, a necessary role in WooCommerce
The shop manager has the same permissions as an editor, with one key difference: they can manage a WooCommerce shop.
As in real life, they can add, edit and delete products, access reports and access certain shop settings (unlike an administrator who has control over everything, as we saw above).
The Customer, the default role for all shops
When a user visits your site and places an order, their information is stored on your site as a customer. They have a dedicated interface in their customer area where they can edit their account details. They will never have access to the WordPress dashboard as you see it.
Are other WordPress user roles possible?
As WordPress is an open-source solution, it is possible to tailor your website to your needs either with plugins (such as Members, an extension developed by MemberPress) or with development knowledge.
Is it possible to modify the permissions of a user role?
As with adding custom roles, it is possible to compensate for missing permissions using coding knowledge or plugins.
The Members plugin, which I mentioned above, provides you with an interface for managing each role separately by granting or denying permissions.
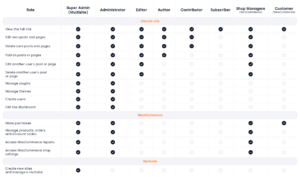
The ultimate cheat sheet for WordPress, WooCommerce, and multisite user roles
To thank you for reading, you can download the WordPress user roles grid in HD PDF format using the button below.